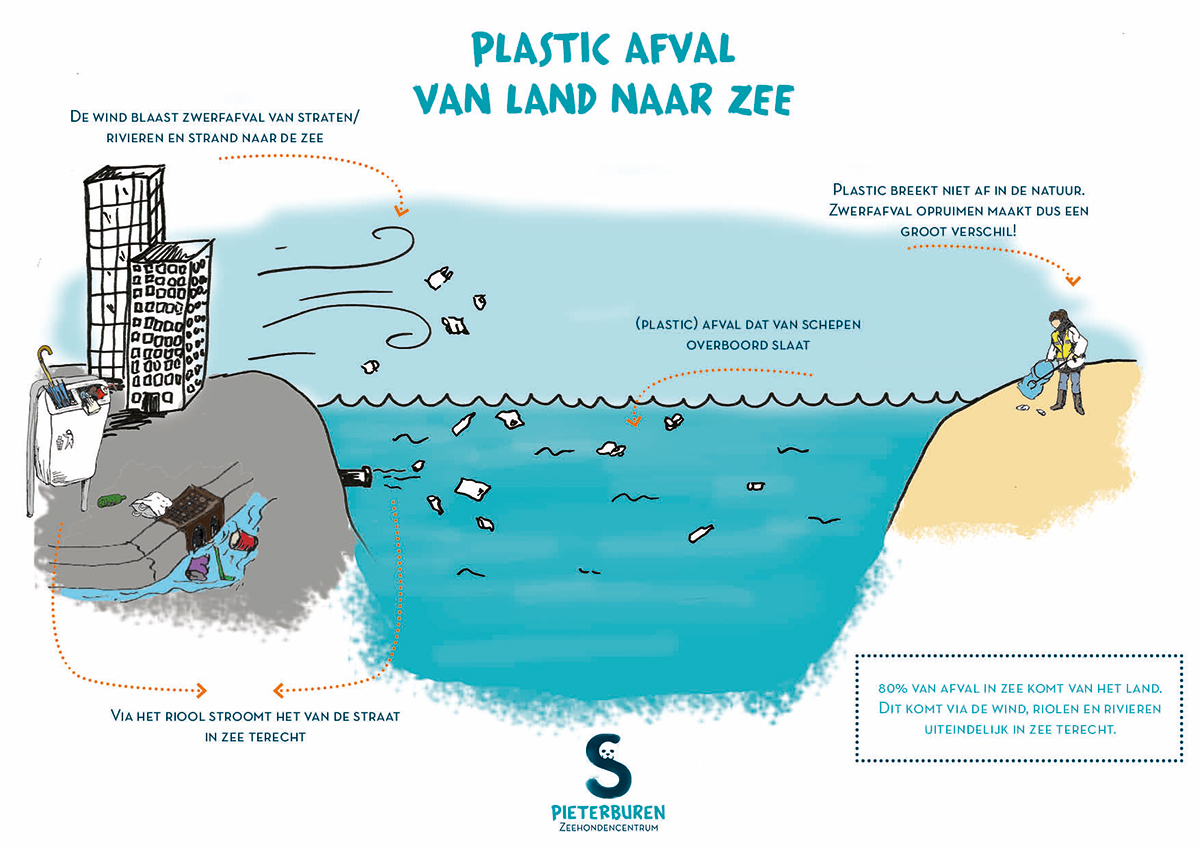
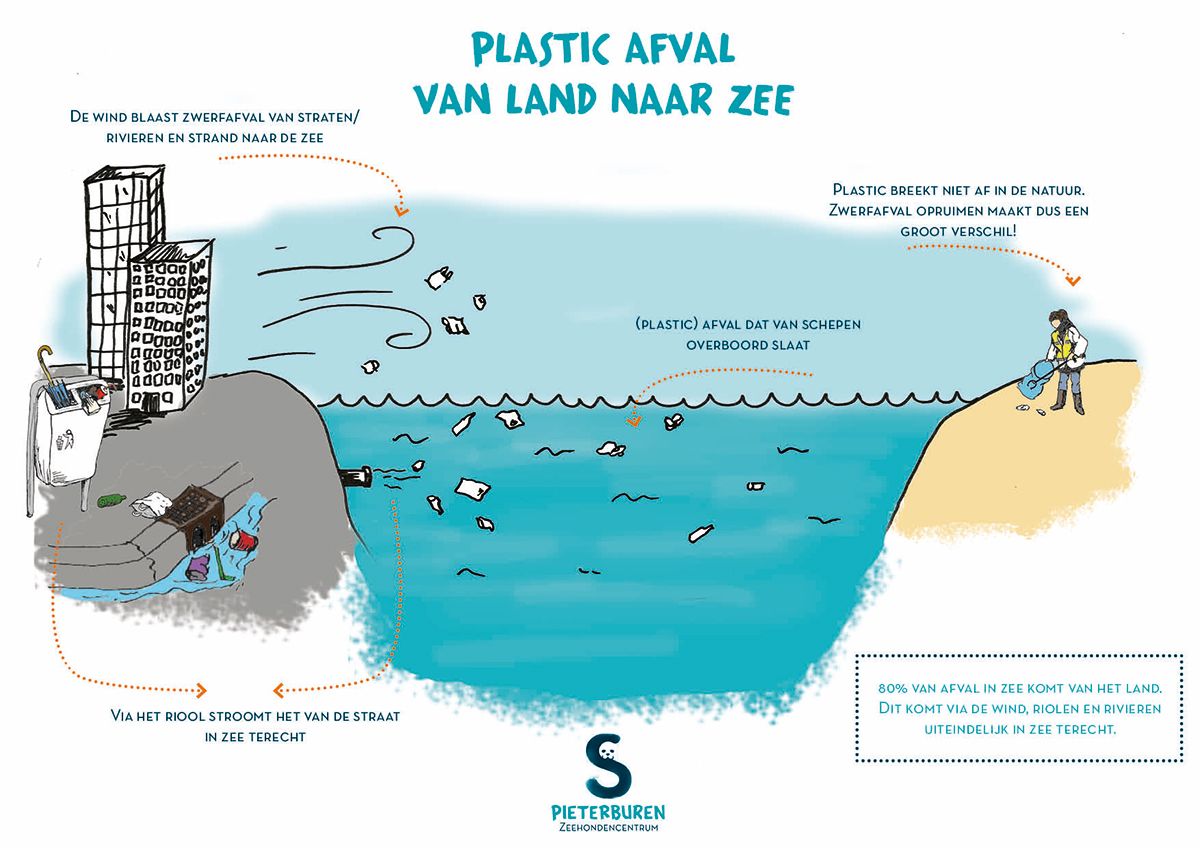
Causes of plastic soup
De mens is de veroorzaker van de plastic soep. Wij maken de plastic producten die uiteindelijk in de natuur belanden. Wist je dat 80% van het afval in zee van het land komt? [1]. Via verschillende omwegen zoals de wind, riolen, grachten of rivieren komt het afval uiteindelijk terecht in zee.
See also
The image shows that a small part of our waste ends up directly in the sea. Most plastic takes a longer route to end up in the water. So something you throw on the street in the city can still end up in the sea.
Plastic pollution for years
Plastic in the sea is (unfortunately) nothing new. Plastic waste has been ending up in the sea for decades. And this will only get more. Every year, 8 billion (!) kilos of plastic waste is added to the sea [2]. Scientists estimate that there are already 150 billion kilograms of plastic in the oceans [3]. At the same time, the world is producing more and more plastic: in 1964, 15 billion kilos were made and in 2014 this had grown to 311 billion kilos of plastic [4].
More and more
So if nothing changes, there will only be more plastic waste in the sea. The shocking prediction of researchers is that if we do not change anything, the seas will consist of more plastic than fish by weight by 2050 [5].
Disposable plastic
The most common plastic waste in the sea is products that you use every day. A striking feature of all these products is that they are single-use plastic: plastic that is thrown away after one use. Figure 3 shows the top 10 most common marine debris. What objects do you sometimes use?

Figure 3: The top 10 most common types of marine litter, by numbers. Bron: https://oceanconservancy.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/FINAL-2018-ICC-REPORT.pdf
Plastic is part of our society
We live in a world where it is unthinkable to live without plastic. Packaging, clothing, cars, care products, electronics: almost everything is (partly) made of plastic. Now it sounds like if plastic is only bad, but did you know that this material also has a lot of georteen?
Plastic material:
- Is cheap,
- Is versatile,
- Can be used for many years,
- Is quite strong [6].
It is precisely these advantages that are also the disadvantages of plastic. Recycling of plastic happens far too little. From 1950 to 2015, only 9% of plastic was given a new life and the rest was landfilled or incinerated to generate energy [7, 8]. In addition, recycling means postponing throwing away a product. This is because used plastic will deteriorate in quality if you want to make it into a complete product again [8].
Plastic can last a lifetime. Plastic that is not recycled can last for hundreds of years and can last even longer if it breaks down into smaller pieces, known as microplastic. Some plastics can even last up to 600 years! [9] If plastic remains floating in the sea for so long, it will continue to pose a threat to marine life now – and in the future.
Sources:
- R. Jambeck et al. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science, 13 february 2015.
- World Economic Forum, Ellen MacArthur Foundation and McKinsey & Company, The New Plastics Economy– Rethinking the future of plastics (2016), Bladzijde 17.
- Ocean Conservancy and McKinsey Center for Business and Environment,Stemming the Tide: Land-based strategies for a plastic-free ocean (2015).
- PlasticsEurope, Plastics – the Facts 2013 (2013);PlasticsEurope, Plastics – the Facts 2015 (2015).
- Projections for 2015 and 2025 based on Ocean Conservancy, Stemming the Tide (2015)
- World Economic Forum, Ellen MacArthur Foundation and McKinsey & Company, The New Plastics Economy – Rethinking the future of plastics (2016),http://www.ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/publications
- Production, use, and fateof all plastics ever made – Geyer et al (2017) https://plasticoceans.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/Production_use_and_fate_of_all_plastics_ever_made.pdf
- Strategy on plastics in the circular economy (2017)European Parlement.
- NOAA / Mote Marine Lab. Approximate Time it Takes for Garbage to Decompose in the Environment.(2017). Available at this link >>